CHROMA 1.0
:: DESCRIPTION
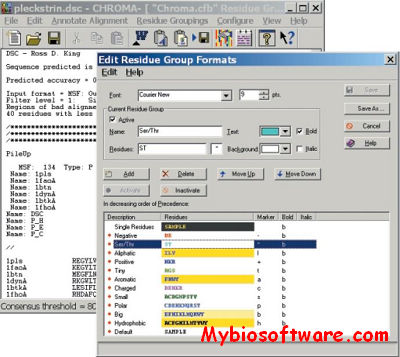
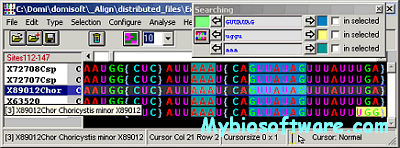
CHROMA is a tool for generating annotated multiple sequence alignments in a convenient format for publication.CHROMA takes your aligned multiple sequence data, annotates residues according to a consensus and displays the alignment using different font formats (text and background colours, bold and italic).
::DEVELOPER
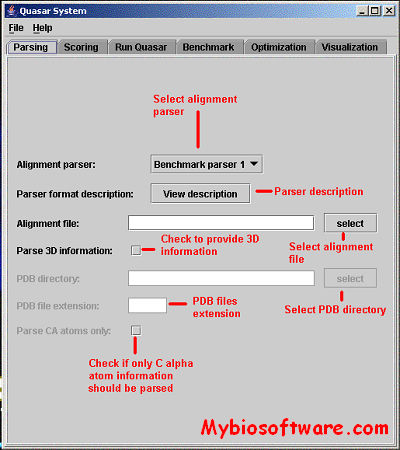
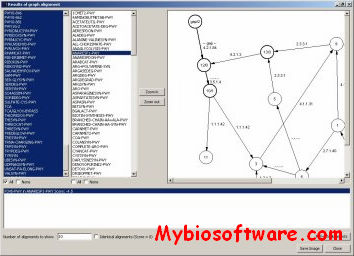
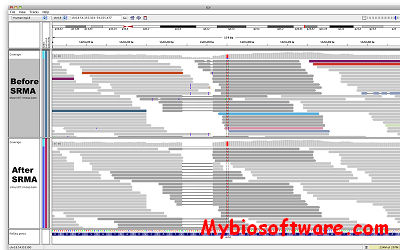
:: SCREENSHOTS
:: REQUIREMENTS
- Windows / Linux
- MS Word
:: DOWNLOAD
:: MORE INFORMATION
Citation
Leo Goodstadt and Chris P. Ponting
CHROMA: consensus-based colouring of multiple alignments for publication.
Bioinformatics. 2001 Sep;17(9):845-6.