DOCK 6.9
:: DESCRIPTION
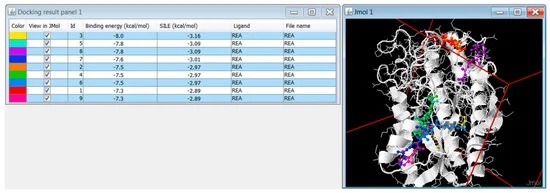
DOCK addresses the problem of “docking” molecules to each other. In general, “docking” is the identification of the low-energy binding modes of a small molecule, or ligand, within the active site of a macromolecule, or receptor, whose structure is known. A compound that interacts strongly with, or binds, a receptor associated with a disease may inhibit its function and thus act as a drug. Solving the docking problem computationally requires an accurate representation of the molecular energetics as well as an efficient algorithm to search the potential binding modes.
::DEVELOPER
DOCK Team
:: SCREENSHOTS
N/A
:: REQUIREMENTS
:: DOWNLOAD
 DOCK
DOCK
:: MORE INFORMATION
Lang, P.T., Brozell, S.R., Mukherjee, S., Pettersen, E.T., Meng, E.C., Thomas, V., Rizzo, R.C., Case, D.A., James, T.L., Kuntz, I.D.
DOCK 6: Combining Techniques to Model RNA-Small Molecule Complexes.
RNA 15:1219-1230, 2009.
 NO
NO