Caryoscope 0.4.0
:: DESCRIPTION
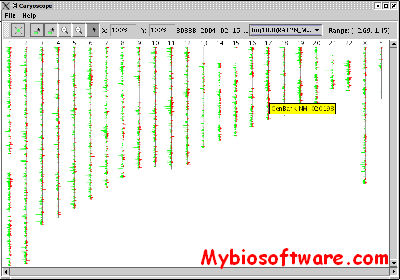
Caryoscope is an application for viewing gene expression data in a whole-genome context. Caryoscope has been used to “draw” microarray data onto a set of chromosomes so that changes in DNA copy number can identify regions of chromosome loss or duplication within the genome of tumor cells (Nat Genet. 1999 Sep;23(1):41-6). In addition, microarray data measuring mRNA expression levels can also be visualized in a genomic context using Caryoscope (PNAS 2002 Dec 10;99(25):16144-9). Data viewed with Caryscope need not be limited to microarray data — any type of numerical data that can be represented as a function of genomic position can be visualized using Caryoscope.
::DEVELOPER
Ihab A.B. Awad, Gavin Sherlock etc.
:: SCREENSHOTS
:: REQUIREMENTS
- Linux / Windows / Max OS X
- JAVA
:: DOWNLOAD
:: MORE INFORMATION
Citation:
.Awad, I.A.B, Rees, C.A., Hernandez-Boussard, T., Ball, C.A. and Sherlock, G. (2004)
Caryoscope: An Open Source Java Application for Viewing Microarray Data in a Genomic Context.
BMC Bioinformatics 5:151.