SnoopCGH Beta
:: DESCRIPTION
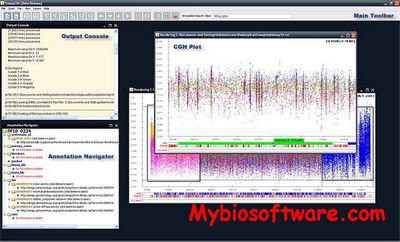
SnoopCGH is a java desktop application for visualising and exploring comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) data. The software allows the user to interactively analyse several sets of data simultaneously. The input is based on a tab-, space- or comma-delimited format, containing series of log intensity values corresponding to one or more comparisons or samples.
::DEVELOPER
:: SCREENSHOTS
:: REQUIREMENTS
- Linux/windows /MacOsX
- Java
:: DOWNLOAD
:: MORE INFORMATION
Citation
Bioinformatics. 2009 Oct 15;25(20):2732-3. Epub 2009 Aug 16.
SnoopCGH: software for visualizing comparative genomic hybridization data.
Almagro-Garcia J, Manske M, Carret C, Campino S, Auburn S, Macinnis BL, Maslen G, Pain A, Newbold CI, Kwiatkowski DP, Clark TG.