NN50-calculator 0.5
:: DESCRIPTION
NN50-calculator (Normalized N50 calculator) is a tool for evaluating the correctness of genome assemblies.
::DEVELOPER
:: SCREENSHOTS
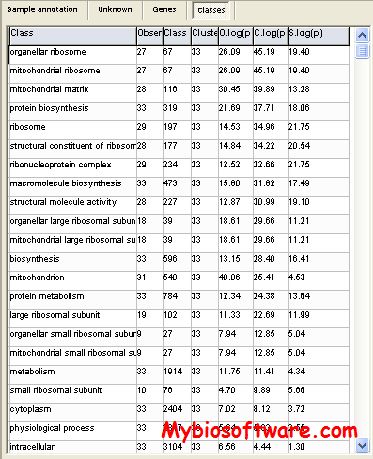
N/A
:: REQUIREMENTS
- Linux
- C++ Compiler
- Python
:: DOWNLOAD
:: MORE INFORMATION
Citation
BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Oct 3;13:255. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-255.
Normalized N50 assembly metric using gap-restricted co-linear chaining.
Mäkinen V, Salmela L, Ylinen J.