Assemble2 2.3
:: DESCRIPTION
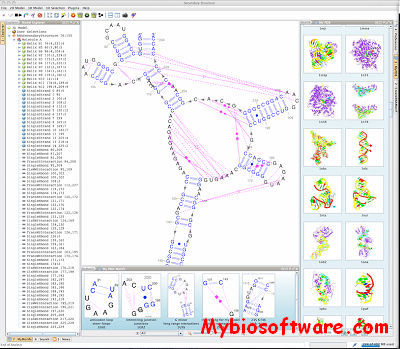
Assemble proposes an intuitive graphical interface to study and construct complex three-dimensional RNA structures. When an RNA tertiary structure is opened with Assemble, it is automatically annotated with a secondary structure definition. This secondary structure can be used as a map to analyze the original tertiary structure. Using a secondary structure definition, Assemble can also produce a first draft of a 3D Model. Then the construction process can be pursued “by hand” using several widgets.
::DEVELOPER
Dr. Fabrice Jossinet at the laboratory of Pr. Eric Westhof
:: SCREENSHOTS
:: REQUIREMENTS
- Windows / MacOsX / Linux
- Java
:: DOWNLOAD
:: MORE INFORMATION
Citation
Assemble: an interactive graphical tool to analyze and build RNA architectures at the 2D and 3D levels
Fabrice Jossinet; Thomas E Ludwig; Eric Westhof
Bioinformatics 2010; doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq321

 NO
NO